Serving as Patrons of the Arts and Literature in Florence Medici
- EXHIBITION THEMES
Celebrated during his lifetime for his extraordinary talent equally a sculptor, architect, painter, draftsman, and poet, Michelangelo inspired subsequent Florentine artists and attracted the metropolis'south nearly powerful patrons—notably the Medici grand dukes. Their extensive and aware patronage allowed art in all media to flourish. In add-on to commissioning portraits and decorative objects for private and public display, the Medici family unit ordered the reconstruction or renovation of numerous civic buildings and private residences and established several major institutions for artistic production and teaching, including Europe's first artists' academy. Cosimo's control of Florence was equally ruthless, but he eventually won the grudging support of the Florentine citizenry––non only for the economical and political expansion he had garnered for the metropolis merely for its greater war machine security. Many also constitute much to adore in Cosimo's wide-ranging intellect, including a deeply rooted involvement in art and literature and a keen fascination with botany, chemistry, and zoology. With an innate instinct for public relations, Cosimo engaged his court painters and the new artists' university, which he helped to found, in the evolution of a repertory of images that communicated Medici power and dynastic dominion. The painters Pontormo (1494–1556) and, to a greater degree, Agnolo Bronzino (1503–1572) fashioned a court portrait style for the Medici, characterized by courtly grace and opulence and often bristling with complex allegories relating to power and armed services might. Bronzino and his workshop produced myriad portraits of Cosimo, Eleonora, and their children; of the grand duke's distinguished ancestors; and of members of the court. A religious discipline by Bronzino commissioned by a member of the aristocracy Medici circumvolve, Holy Family with Saint John the Baptist , is ane of the painter's most historic works. Its references to specific examples of ancient Greek and Roman sculpture—which the artist had seen during a recent trip to Rome—were surely recognized and appreciated by the learned patron and his colleagues. Pontormo, primarily a painter of religious subjects, was awarded numerous important commissions by Cosimo, including the decoration of the choir of the Medici church building of San Lorenzo (1546/51). Now lost, the imaginative and unusual San Lorenzo frescoes are known primarily from Pontormo'south surviving preparatory drawings, on view in the exhibition. These studies give some sense of the peculiar, personal nature of the lost paintings. Gardens and fountain sculpture were among the glories of Medici patronage. Cosimo appointed Niccolò Tribolo to redesign the gardens of the Medici villa at Castello (outside of Florence) and the Boboli Gardens (behind the Palazzo Pitti) with fountains, grottoes, water tricks, and areas of trimmed and wild plantings. Giambologna's bronze effigy of a woman wringing water from her hair, variously identified every bit either Florence or Venus, once graced a fountain in the garden of the villa at Castello. back to summit Michelangelo's works from this period represent a new figurative style that the painter and author Giorgio Vasari (1511–1574) called maniera (Mannerism), characterized past expressive ability and complex, yet elegant, class. Among the sculptor'south nigh singular innovations is the figura serpentinata (serpentine figure), in which a small caput tops a massive muscular torso and tapering thighs, and the trunk dynamically twists so that its musculature can be viewed from many angles. This concept, its implied motility augmented when viewed from all sides, connected to influence sculptors and painters throughout the belatedly-Renaissance and Bizarre eras. The pose of the clay (terracotta) Male Torso attributed to Michelangelo is consistent with the torsion seen in works by the master and his followers. It may have served as a model for a marble or a bronze cast. The wooden Crucifix , probably incomplete at the fourth dimension of Michelangelo's expiry in 1564, represents the spare, elongated style of the creative person'southward final years. The crude forms, unfinished surfaces, and introverted mood relate to some of his almost moving drawings of Crucifixion scenes. back to summit dorsum to top back to top The complex decorative program for the pocket-size sleeping accommodation, conceived by the learned Vincenzo Borghini, head of the artists' university, was as treasured as the objects stored and had as its primary theme the dynamic relationship betwixt art and nature. Personifications in the Studiolo's ceiling frescoes related this theme to the four elements, the four seasons, and the four temperaments. Organized mainly according to their affiliation with the iv elements––globe, air, fire, and water––the prince's objects and materials were deposited in 19 cupboards distributed along the 4 walls. Covering or side by side to each chiffonier was a panel with a painted representation of a scene––religious, mythological, historical, or industrial––that in some way referred to the closet's contents. For example, Mirabello Cavalori's Wool Mill , which shows the processing of wool in cauldrons boiling over high flames, would have been located on the fire wall, and alum, a chemical used in the handling of wool, would have been kept in the cupboard below Cavalori's picture. Pearls, coral, and other objects associated with the sea were kept in cabinets on the water wall near related paintings. Francesco'due south collections apparently outgrew the Studiolo quickly, and the room was dismantled in the late 16th century. The dispersed paintings and sculptures were reassembled in the early 20th century, but the room was incorrectly reconstructed. The study room in the exhibition and the catalogue essay on the Studiolo offering a new proposal for the arrangement of the decorations and for the identification and placement of the contents in the cupboards. The various geological and zoological specimens on brandish in the study room were non themselves part of the prince's collection just are examples of the sorts of materials Francesco is known to have stored in his Studiolo. dorsum to top The 1000 Duke ceaselessly encouraged artistic collaboration and innovation among his artists and craftsmen. He hired Milanese jewel engravers to brand Florence an important center of pietre dure (difficult-rock) etching. He brought in goldsmiths and jewelers, such as Jaques Bylivelt from Delft, to create works of precious metals, including jewel-like mounts for hard-rock vases. About chiefly, Francesco appointed Bernardo Buontalenti, an immensely talented designer and architect, to serve equally creative manager of the workshops. back to superlative In 1587 Francesco I died without a legitimate male person heir, and Ferdinando, who had never taken priestly vows, immediately declared himself the third Grand Duke of Tuscany. Seeking a marriage that would preserve his political independence, Ferdinando chose his distant cousin, Christine of Lorraine, the favorite granddaughter of Catherine de' Medici, Queen of France. The sumptuous and well-documented hymeneals festivities, celebrated in Florence in 1589, were designed to impress the majestic houses of Europe. The wedding anniversary in Florence Cathedal was followed by outdoor events for the public, too as banquets and balls, comedies and musical interludes, and a mock sea battle in the flooded courtyard of Palazzo Pitti for the aloof guests. Altogether the wedding spectacles cost approximately seven million dollars in today's currency. These lavish and innovative forms of entertainment proved to be more than than showmanship. They greatly influenced theatrical practices in European courts throughout the 17th century. dorsum to top With Ferdinando's steady patronage and encouragement, pietre-dure workers became experts at manipulating color variations in stones of complex shapes to achieve a painterly effect in their designs. These skills were applied to create elaborate mosaics in manners both naturalistic and stylized. The onetime mode is exhibited in the oval plaque showing the Piazza Granducale, with its remarkable illusion of book and depth. The mosaic of the Medici-Lorraine coat of artillery, probably created at the time of Ferdinando's wedding to Christine of Lorraine, displays the flatter mode of heraldic subjects. dorsum to superlative Cosimo 2 upheld the reputation of the Medici as patrons of the natural sciences and the arts. He appointed Galileo Galilei to professor of philosophy and mathematics at the University of Pisa. In return Galileo named the iv Jupiter moons he discovered in 1610 the "Medici stars." Cosimo used his family'due south weddings, birthdays, and anniversaries every bit opportunities to promote performing arts. He spent lavishly on court entertainment, equestrian performances, and theater. In times of peace, his courtiers displayed elaborately chased arms and armor at sporting tournaments, a number of which are on view in the exhibition. The reigns of the first four Medici one thousand dukes coincided with the Counter Reformation, the movement that arose within the Catholic Church to clarify its doctrines, especially in relation to Protestant tenets, and to address the abuses of power past its clergy. The Yard Knuckles demonstrated his piety and responded to the impact of the Counter Reformation through commissions executed in the sumptuous style favored by his court. Especially lavish use of precious materials, rich color and textures, and intricate decorative motifs distinguish the clerical garments, liturgical objects, reliefs, and paintings of sacred themes produced during Cosimo II's reign. Religious art commissioned during the Counter Reformation by the Medici and other prominent Catholic rulers had a special significance as Catholic reforms continued well into the side by side century, and the Church renewed its accent on art as a powerful instruction tool. dorsum to top Following Cosimo II'south death in 1621 at the age of thirty, his wife and female parent served as co-regents for his son Ferdinando II, then simply x years erstwhile. Past the time Ferdinando succeeded to the title, Florence'south fortunes had begun to fade. The 1000-ducal treasury was severely depleted, and a period of austerity reduced cultural initiatives. Many artists chose to leave Florence for Rome, Naples, and other cities where the new Baroque style was rapidly ascending. Beginning with Cosimo I, the Medici g dukes were arguably the starting time political leaders in Europe to institute modernistic systems of urban planning and to use cultural commissions to celebrate their accomplishments and secure their dynasty's future. Through their all-encompassing patronage initiatives—resulting in new residences, government centers, fortified compounds, artistic institutions, gardens, public sculpture, fountains, and elaborately staged events—the starting time Medici one thousand dukes dynamically transformed Florence and exerted a widespread and lasting cultural influence on other European courts.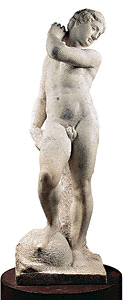 The Medici, Michelangelo, and the Fine art of Tardily Renaissance Florence provides a detailed survey of the art and culture of 16th-century Florence, the crucible of the Italian Renaissance. Between 1537 and 1631, the showtime iv Medici thousand dukes—Cosimo I; his sons, Francesco I and Ferdinando I; and his grandson, Cosimo Ii—presided over a spectacular flowering of the arts and sciences, exemplified by the pioneering achievements and dominant legacy of Michelangelo.
The Medici, Michelangelo, and the Fine art of Tardily Renaissance Florence provides a detailed survey of the art and culture of 16th-century Florence, the crucible of the Italian Renaissance. Between 1537 and 1631, the showtime iv Medici thousand dukes—Cosimo I; his sons, Francesco I and Ferdinando I; and his grandson, Cosimo Ii—presided over a spectacular flowering of the arts and sciences, exemplified by the pioneering achievements and dominant legacy of Michelangelo.
In 1537 the young Cosimo de' Medici (1519–1574) was plucked from relative obscurity in the Tuscan countryside to lead Florence after the assassination of his cousin Duke Alessandro de' Medici (1511?–1537). Surprising the Florentine aristocrats who put him in ability, who believed they could hands manipulate the 17-year-old, Cosimo declined to marry into 1 of their families. Instead, he tied himself firmly to the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V (1500–1558) by marrying the Spanish princess Eleonora di Toledo (1522–1562), daughter of the emperor's viceroy in Naples. In so doing, he elevated himself to accented ruler of Florence. By 1569, when Cosimo convinced Pope Pius V (1504–1572) to bequeath on him the title of Grand Knuckles of Tuscany, he had expanded his totalitarian rule throughout the Tuscan territories, sometimes violently seizing command of neighboring cities.
Michelangelo always pushed the limits of the possible, infusing his art with his soul and intellect. He was often more than concerned with the exploration and solution of an artistic trouble than with the finished piece of work. One of his greatest and near influential projects in Florence, left incomplete when he departed for Rome in 1534, is the burying chapel, or New Sacristy, in the Medici church of San Lorenzo. The chapel includes a number of greater-than-life-sized marble statues, among them the famous personfications of the four times of day (Day, Dark, Dawn, and Sunset). During the 1520s and 1530s, Michelangelo carved most of the New Sacristy sculptures besides every bit Apollo/David . It is unclear whether Michelangelo originally intended the latter to represent the biblical hero David, holding his sling, a symbol of the Florentine republic; or if the artist planned to finish the marble as Apollo, the sun god, reaching dorsum for an pointer (and who would afterwards become the emblem of the Florentine art academy and its patron, Cosimo).
In the offset half of the 16th century the finest tapestries in Europe—prized by royal and aristocratic collectors—came from Flanders, specially Brussels and its surrounding area. In 1545 Cosimo decided that Florence, already distinguished every bit a heart of textile production, would rival Brussels in the fine art of tapestry weaving. After hiring Flemish artisans to manage his workshops, he called upon some of the foremost Florentine artists of the mean solar day—Agnolo Bronzino, Jacopo Pontormo, Francesco Salviati—to provide cartoons (full-scale designs) for tapestries, steps that quickly resulted in a remarkably high quality of craftsmanship and artistry. The theme and imagery of the portiera (door hanging) designed by Bronzino, Abundance , suggests the marvelous compensation enjoyed by Florence nether Cosimo'south rule.
Upon the expiry of Cosimo I, in 1574, his son Francesco (1541–1587) became the second Grand Duke of Tuscany. Less defended to statecraft than his male parent and naturally introverted, Francesco never emerged from the shadow of Cosimo's long reign or achieved a political persona of his ain. For years Francesco was reprimanded by his begetter for spending his time in laboratories and workshops by day and taking solitary walks nearly the urban center by night. Lacking Cosimo'south social ease and spontaneity, Francesco imposed a rigid decorum on his courtroom and congenital secret rooms and passageways so that he could move nigh the 1000-ducal residences and the urban center undetected. Like his father, Francesco was fascinated with the applied sciences and was obsessed with the study of abracadabra and medicine—the latter partly in order to treat his ain melancholy, or chronic low. He besides continued the Medici patronage tradition, encouraging the fine and decorative arts.
In the winter of 1569–70 Francesco deputed the ornament of a small room that would become his master legacy––the and so-called Studiolo in the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence. The Studiolo, created by Giorgio Vasari, was a hidden vault room in which the young prince stored his collection of minor, precious, unusual, or rare objects and materials. Francesco'southward myriad interests ranged from alchemy to zoology and included such fields as geology, glassmaking, and metallurgy.
Francesco imported talented craftsmen from other parts of Italy and northern Europe to produce luxury objects in Florence. For instance, he invited the maiolica painter Flaminio Fontana from Urbino and potters from Faenza to establish a porcelain workshop, which became the offset European manufactory to succeed in producing ceramics in faux of Chinese porcelain. (Hard-paste, or "true," porcelain of China differed technically from the soft-paste ceramic ware of Florence, but variations in translucency, whiteness, and hardness are barely detectable.) The Medici ewer, one of the largest, most beautifully decorated, and historically of import examples of the technique, is featured in the exhibition, along with the best Medici porcelains in American collections, each slice unique and masterfully designed.
Born in 1548 as the fourth son of Cosimo I and Eleonora di Toledo, Ferdinando de' Medici (1548–1609) originally was not intended to dominion. In 1563 he became a key and moved to Rome, where he continued his father'southward history of artistic patronage. He enlarged and embellished the magnificent Villa Medici to firm his superb drove of classical sculptures, later to be installed in the Uffizi Galleries in Florence.
Ferdinando was especially passionate about pietre dure, in part because he wished to adorn a number of the stately interiors of his residences with panels in this rich and difficult medium. He created a special pietre-dure workshop and elevated it to a level of importance in a higher place artisanal studios. The Galleria dei Lavori (Gallery of Works), later renamed the Opificio delle Pietre Dure (Hard-Stone Industry), chop-chop won international acclaim for its magnificent products, and it still exists today.
Born in 1590, the son of Ferdinando I de' Medici and Christine of Lorraine, Cosimo II's comparatively cursory reign (1609–1621) was a period of peace and prosperity for Tuscany, cheers largely to the political and economic policies his father and gramps had put in place. Cosimo's spousal relationship in 1608 to the Archduchess Maria Maddalena of Republic of austria (1587–1633), sister of Emperor Ferdinand Two, centrolineal the Medici family unit with the powerful Habsburg dynasty.
Cosimo II inherited his family unit'due south interest in fine art patronage for the glorification of the dynasty, and he significantly augmented the Medici collections. His acquisitions reveal a wide-ranging involvement in gimmicky painting, from Florence and elsewhere, and an ongoing commitment to the Medici workshops. These establishments continued to produce luxurious objects, with a gradual shift from the complex and intricate Mannerist designs of the Florentine courtroom artists to the bold, dramatic language of the Baroque. All the same, in paintings such every bit Judith with the head of Holofernes past Cristofano Allori (1577–1621), this new style thrived in the glamorous trappings of the Florentine court.
Reproduction Permission . Copyright © 2002. All rights reserved.
Source: https://archive.artic.edu/medici/themes.html
0 Response to "Serving as Patrons of the Arts and Literature in Florence Medici"
Post a Comment